Wide-Angle Polarimetric Camera (PolCam)
PolCam, a Wide-Angle Polarimetric Camera, is onboard the Korea Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter to investigate the lunar surface based on polarimetry. PolCam will construct a global lunar map of polarimetric parameters.
The Korea Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter (KPLO), Danuri, has been launched on August 5th, 2022. KPLO is orbiting the Moon at an altitude of 100 ± 30 km during the nominal mission of up to 12 months including the commissioning phase. The objectives of the KPLO mission are to develop critical technologies for lunar exploration and deep space communications, to scientifically investigate the environment of the Moon, and to realize and validate new space technologies such as space internet. The scientific payload of the polar orbiter includes the Wide-Angle Polarimetry Camera (PolCam), Lunar Terrain Imager (LUTI), KPLO Gamma-Ray Spectrometer (KGRS), KPLO Magnetometer (KMAG), Disruption Tolerant Network (DTN), and ShadowCam.
PolCam will measure the polarimetric properties of the lunar surface including those of the far side for the first time. Systematic polarimetry of the Moon has been performed using only ground-based telescopes on Earth. The median size of surface particles and their internal opacity can be estimated from polarimetric measurements. However, observations from Earth have inherent limits of available phase angle, resolution, and observable area of the Moon. To overcome these limitations, the KPLO/PolCam will observe the surface of the Moon from lunar orbit.
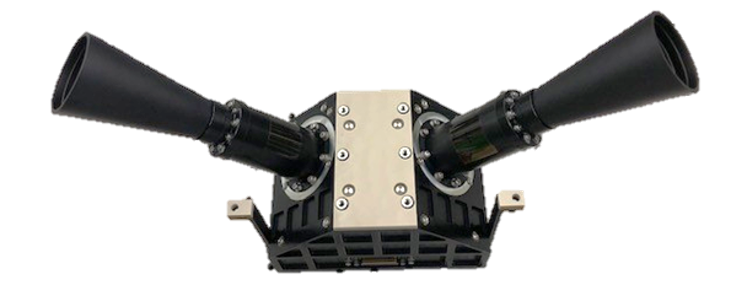
[ PolCam's optical unit ]
PolCam will construct a global lunar map of polarimetric parameters, such as maximal polarization (Pmax) and titanium distribution using three color bands centered at 320, 430, and 750 nm. PolCam?s twin cameras are mounted at 45° tilt angles from the nadir across the orbital track in opposite directions.
PolCam will obtain polarimetric measurements of sunlight scattered by the lunar surface at various phase angles up to ∼140° to achieve the scientific goals during the one-year mission. Since degree of linear polarization is a function of phase angle, it is essential to perform several measurements at various phase angles to properly retrieve, e.g., Pmax, Pmin, and the inversion angle, αinv.

Contact: Dr. Chae Kyung SIM (cksim [at] kasi.re.kr)